Summary:

Field Studies
This is by far my favorite form of user research. Being able to observe users in their most natural environments without interfering feels like such an incredible opportunity. In that moment you forget yourself and instead become completely neutral, unbiased and fully focused on your subject.
The goal of this type of study is to remain as non-obtrusive as possible. Keep engagement to a minimum, do not give opinions or express strong emotions that could introduce unecessary bias into your study. Take notes, pictures, and videos (with the permission of your subjects) in the least disruptive way possible.
Each movement, gesture, sound, etc is noteworthy as you wont know until after the study what critical insight was given in that moment. It's fascinating to be able to have this level of access to any user group and companies should do their best to invest efforts into this type of study.
Field studies are invaluable when it comes to creating empathy maps, user personas, and user journeys. These types of studies are gold mines for any UX researcher.
User Testing
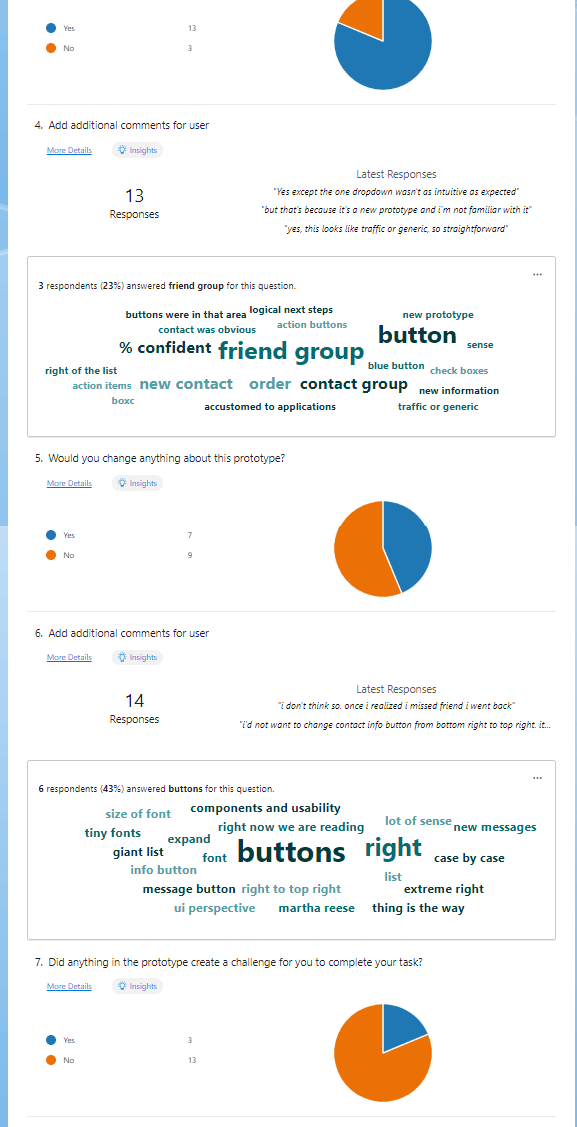
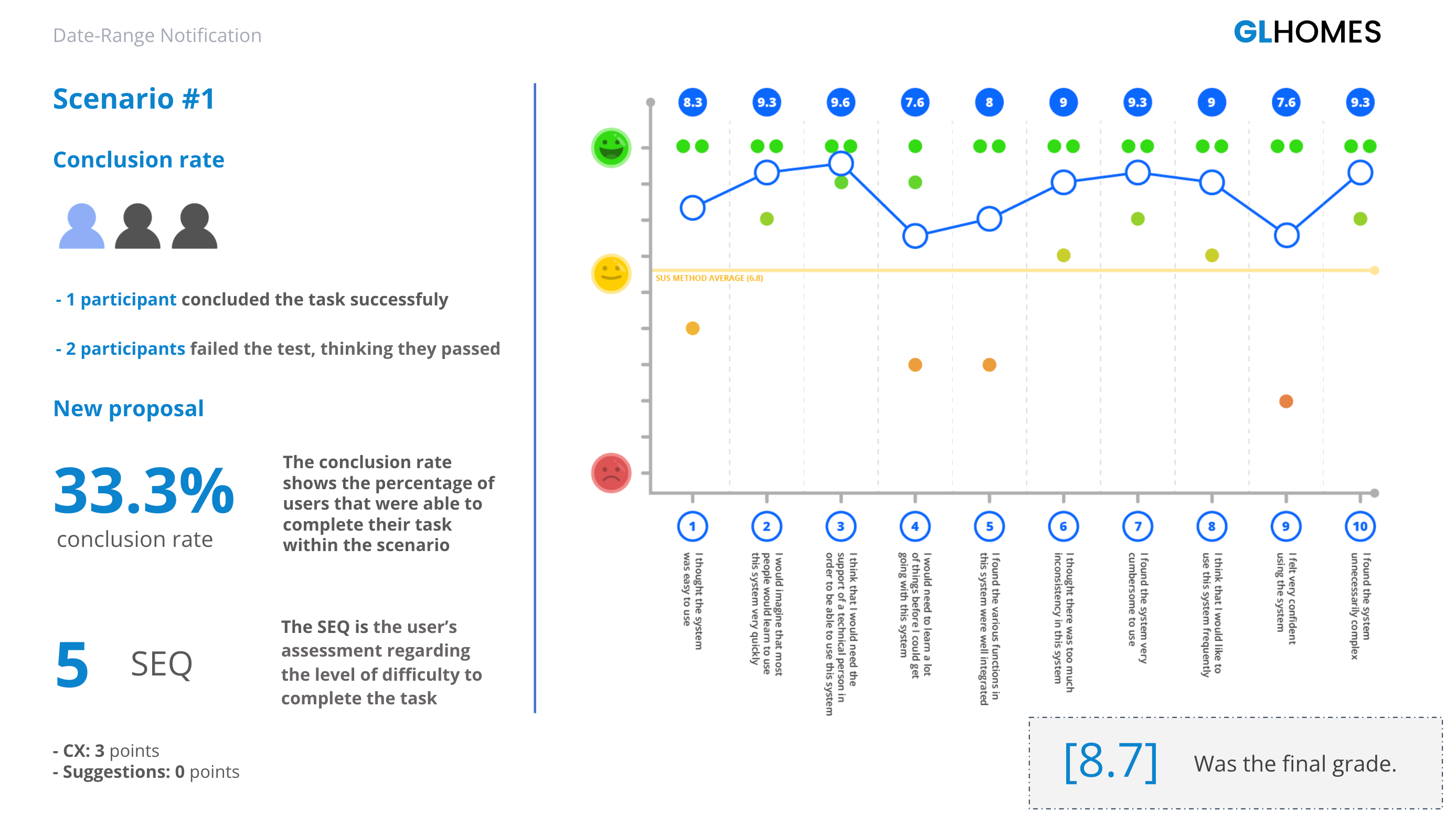
To increase the success of a product or feature you must validate your designs with your end user. These tests can be done either in person or virtually. If you're able to observe your user while they interact with your design prototypes that's evven better. Users can test your designs at any stage of wireframing from sketches, mid-fidelity, to fully designed interactive prototypes. The goal is test early and often.
Users aren't just limited to paying customers. Developers and business stakeholders are also users who need to be invovled in the design and ideation process early on. Understanding their needs and concerns throughout the process will ensure you are meeting business and development needs as well. If you can, try to include developers or business stakeholders in a few end user interviews. This will help them develop a deeper understanding of their customers and add a human factor to the products they are developing.
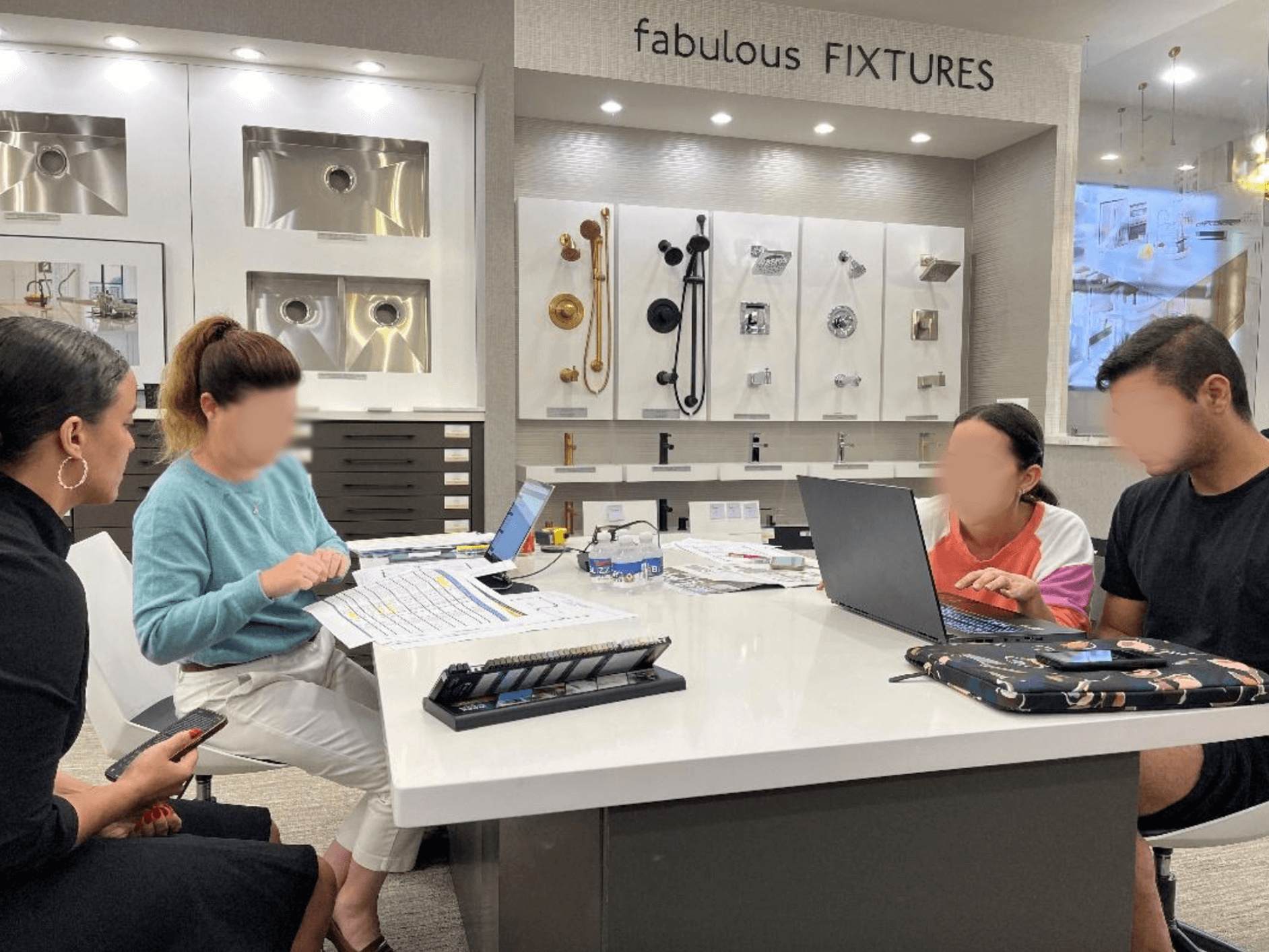
User Interviews
To successfully conduct a user interview does require a good amount of strategic hospitality. Can you disarm your subject enough for them to trust you and reveal critical information needed for the success of your product? Being able to assess your user on sight and control the conversation without feeling directive takes tact.
The good news is these skills can be learned and as we all know nothing beats practice. The more you do something the more natural it becomes. A great solution is to go into your interview prepared. Do as much research as you can about your user, have your questions ready, explain the agenda to your subject, and be mindful of any drawn-out tangents. Being able to steer the conversation back to the subject at hand can be done gently by simply asking the subject their thoughts on the topic.
Analytics Tracking
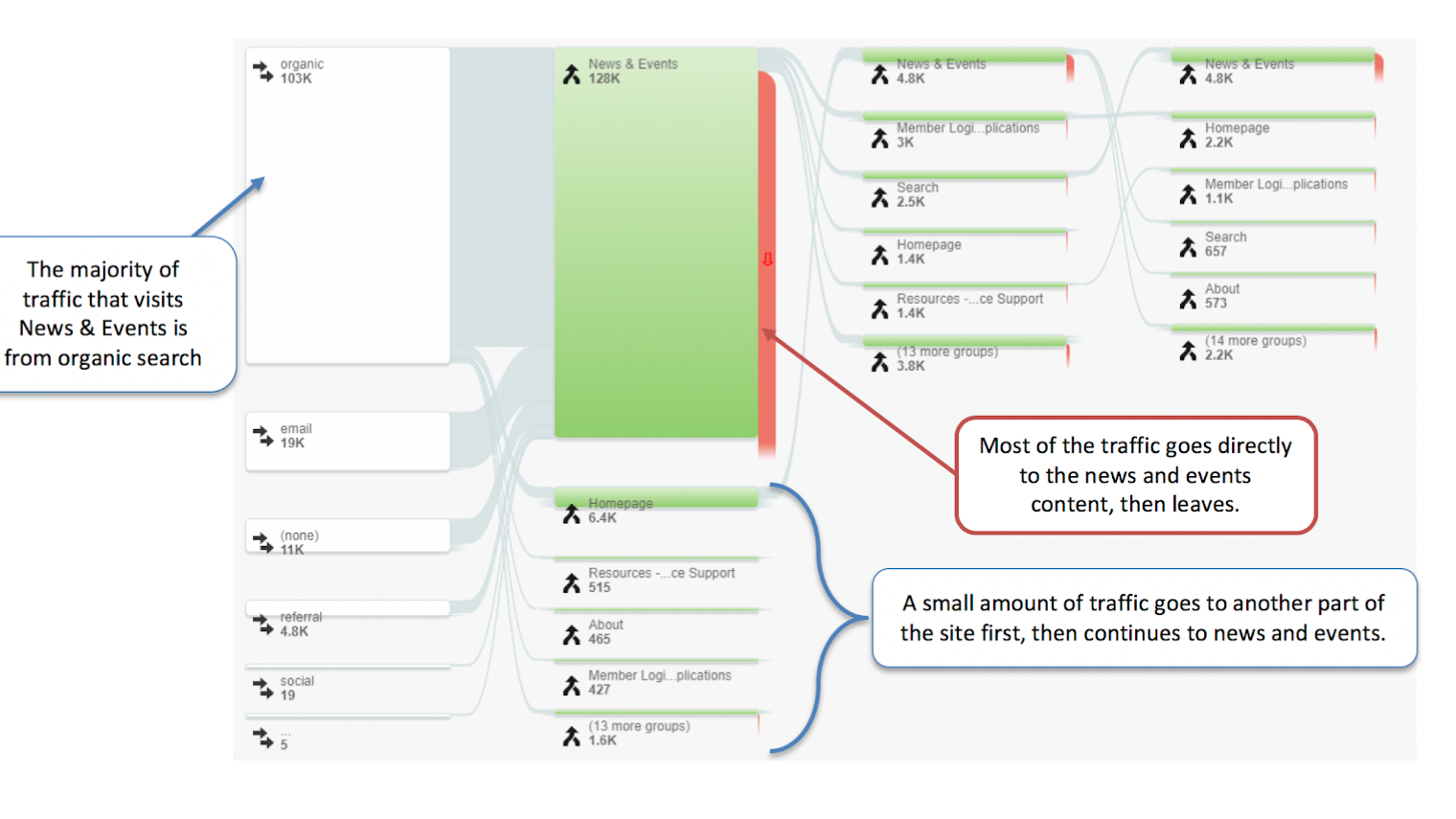
Reviewing data from web analytics are a great way to gather research for a digital product. Setting up tracking for user bahavior, click-through rates, and sales funnels allows teams to develop more informed strategies for sales and information architecture.
Giving the UX Specialist access to site analytics helps them see how successful their designs and interactions are with their end users. Being able to drill down into user flows helps illuminate areas that need improvement in guiding users to the products they desire.
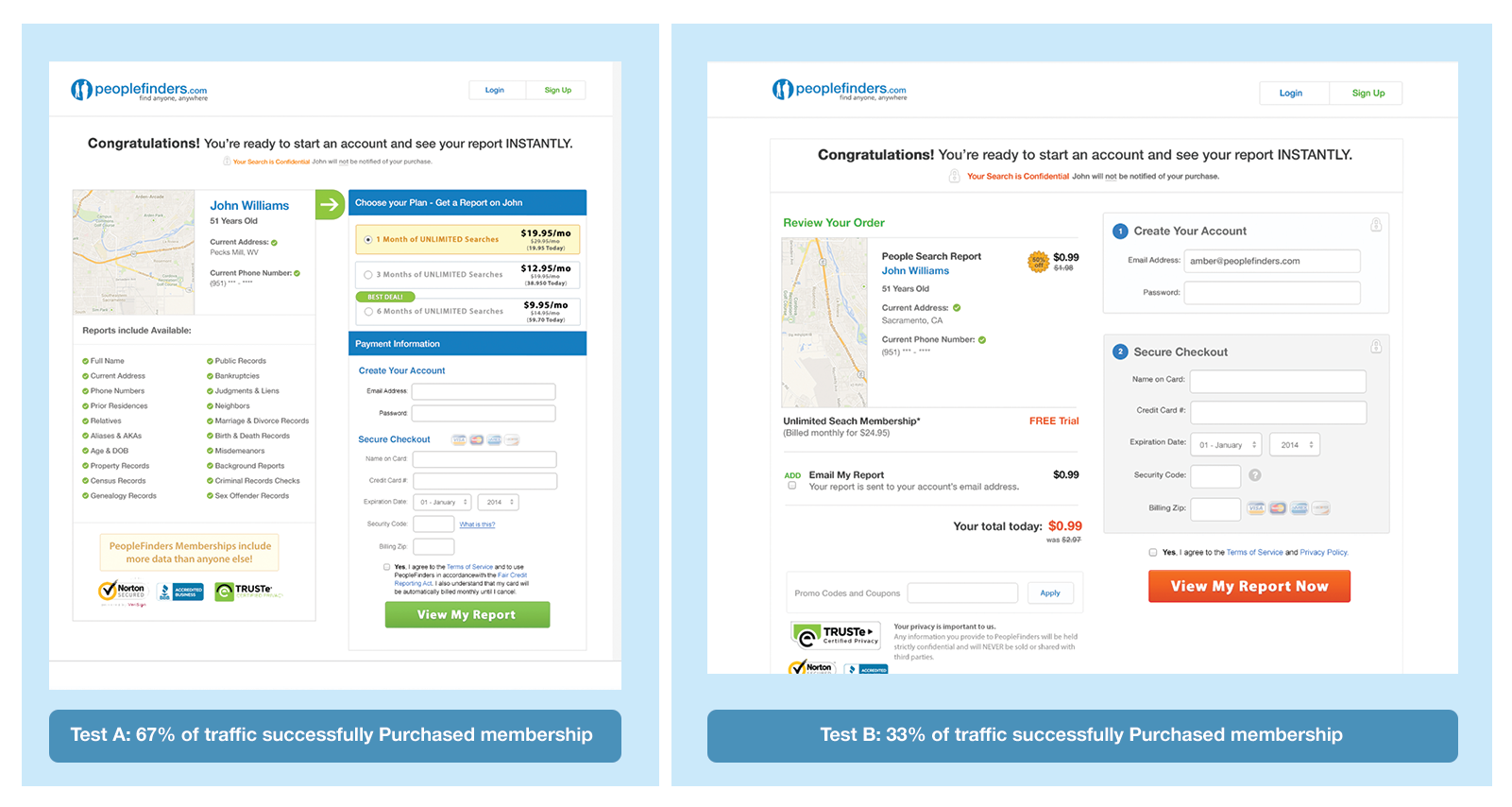
A/B Testing
User behavior can be unpredictable and when it comes to making sales it's not uncommon for businesses to A/B test their product or checkout pages. By doing this you're able to quickly and seamlessly increase profits by simply changing a button color, rewording a sales pitch, or adding an image that represents your user demographic.
By splitting what your audience sees you are recieving unbiased data on what your users want.